- Home
- Sustainability
- Environment
- Approach by Businesses Toward Environmental Conservation
- Global Warming Prevention Activities
Sustainability
Environment
Approach by Businesses Toward Environmental Conservation Global Warming Prevention Activities
For the purposes of global warming prevention work, OKI Group sites are classified into different categories to enable prevention measures tailored to the characteristics of each category. The categories are processing plants (mostly for painting and plating), product assembly plants (mostly for mounting parts), large offices and small offices.
Processing plants
Challenge to achieve both delicate quality control and CO2 reduction in the press process
Stainless steel spring steel sheet requiring higher quality
Dedicated device using Hydraulic motor used for bending stainless steel spring steel sheet
At OKI Sympho-Tech Co., Ltd. (OSC), which consists of two businesses: sheet metal processing for outdoor housings and custom power supply manufacturing, we reviewed the operating methods of press equipment used in metal bending, which is our specialty, and obtained significant effects in reducing CO2 emissions and costs.
The bending of some products (stainless steel spring steel plates), which require higher quality, is performed by a special equipment using a hydraulic motor. However, if the temperature is not kept constant, the volume of oil will change and even if the product is processed at the same pressure, the bending finish will change significantly. The hydraulic pressure of the motor varies from 500 grams to more than 100 tons depending on the thickness and length of the metal to be bent, the material to be bent, and the angle to be bent. However, if the adjustment is incorrect, the material will bend back the moment the pressure is released after work, which is known as a spring back problem.
For this reason, the company had to leave the equipment in standby mode for quality reasons. In this project, by optimizing the standby time of press equipment while ensuring quality, we succeeded in reducing electricity and CO2 emissions by approximately 80% and ensuring quality with this equipment alone.
90% Energy Savings in Continuously Operating Equipment
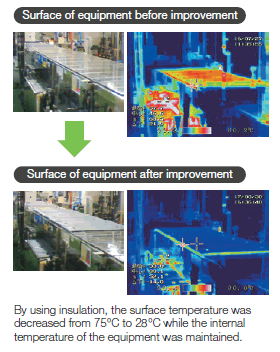
OKI Circuit Technology (OTC), which manufactures high-reliability printed circuit boards etc. used in space, is promoting the reduction of fixed energy consumption in production facilities that operate non-stop.
One of these, the desmear processor, is equipment that melts and removes the shavings (smear) remaining on the drilled surface of the board, and constantly consumes electric power. Since a large amount of heat is emitted by the equipment when maintaining the interior at a high temperature for the melt treatment, gas was necessary for supplying steam for heating and maintaining the inside temperature of the equipment, and electric power was required to cool the room and prevent the temperature from rising around the equipment, which was a problem in terms of energy conservation.
As a countermeasure, we succeeded in suppressing the external heat release and reducing the surface temperature from 75℃ to 28℃ by covering the surface of the equipment with a heat insulating material. In order for it to be able to withstand the heat of the equipment, we selected a heat insulating material made of fluororesin and glass fiber. Thanks to these measures, we reduced the energy by an equivalent of 94% of the conventional equipment alone and succeeded in reducing costs.
Improvement of Energy Efficiency Through Review of Air Conditioning Balance
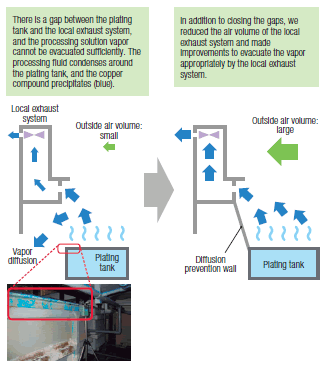
In the copper plating room of OKI Circuit Technology, the exhaust system used to operate at full power, but it produced a strong and unique odor, which was a problem. As a result of a survey, two reasons were identified concerning the dedicated exhaust system (local exhaust system) which evacuates the processing solution vapor emitted by the plating tank.
(1) There was a large gap between the local exhaust system and the plating tank, through which the vapor of the processing solution escaped, and copper compound was precipitated around the plating tank.
(2) While the local exhaust system air volume was set too high, the amount of outside air entering the room was small and sufficient ventilation was not achieved, resulting in vaporized chemical substances diffusing inside the room.
With respect to (1), a diffusion prevention wall was established as a countermeasure, and for (2), the balance between the volume of the local exhaust system and the amount of outside air entering the room was adjusted to achieve the proper flow of air to the local exhaust system.
Through these measures, we promoted an improvement in the work environment, a reduction in environmental impact, an improvement in energy efficiency of the local exhaust system etc., and a reduction in production costs.
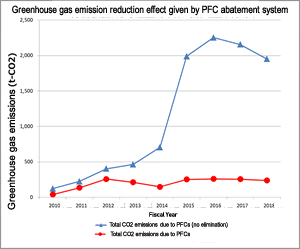
PFC greenhouse gas elimination rate of at least 99%
OKI's LED plant has started using dry etching processes to increase the competitiveness and improve the quality of the semiconductor devices it produces. Some of these processes use greenhouse gases called PFCs as reaction gases. Reducing emissions of these gases is a key issue since they are decomposition-resistant and have high global warming potentials (GWPs) of about 7,000 to 20,000 or more.
The plant has taken aggressive measures against global warming. In FY 2015, it started installing abatement systems designed to break down PFC gases as one way of reducing greenhouse gas emissions caused by these gases.
The systems have been highly effective, attaining an elimination rate of at least 99% in a sampling-based performance assessment. (The OKI Group's estimates of greenhouse gas emissions are calculated using a figure of 90%, in conformance with the value of 'at least 90%' given by the abatement system manufacturer.)
Product assembly plants
Energy-saving Using Projection Mapping
Issues with high-mix low-volume manufacturing / multiple parts
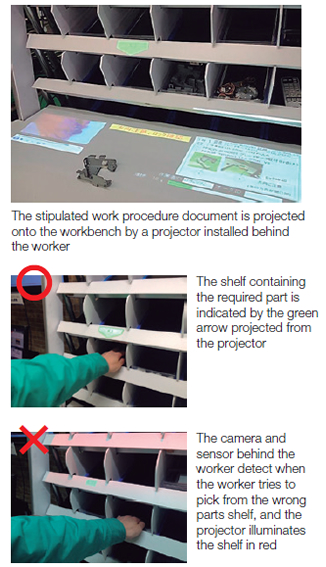
OKI’s Mechatronics System Plant manufactures ATMs, cash handling equipment, check-in terminals and the like. The plant handles as many as 10,000 pieces, the largest number in the OKI Group. In order to produce a high-mix lowvolume manufacturing in accordance with the specifications of each customer, the accurate picking of parts without omission by workers posed a challenge to raising the proficiency and efficiency of work.
A system to support the passing on of skilled techniques
Accordingly, we realized a parts picking system applying projection mapping technology to project images in 3D.
When starting work, this system projects a stipulated work procedure manual from a projector onto the workbench. If the worker moves to take the necessary parts from the shelf according to the procedure manual, a green arrow and a number projected from the projector indicate which shelf the part is on how many to take. The camera and sensor behind the worker detect when the worker places a hand on the wrong parts shelf, and the color of the shelf turns red. In addition to this, functions that inform of real-time improvements in work efficiency based on motion analysis are incorporated, accelerating the acquisition of skilled techniques and improvements on the shop floor.
1/4 the investment, 1.5 times the energy efficiency
In the previous system, detection LEDs and sensors were installed on each part shelf, making the apparatus complicated and costly.
The current system has improved the energy consumption rate, which expresses production efficiency, by 1.5 times while reducing capital investment to 1/4 of the previous system. This leads to energy-savings and cost improvements.
"Solder Revolution" Yields Reduction of 70% in Power and Resource Consumption

Point DIP machines that solder the exact locations necessary have reduced environmental burden by 70% at OKI Nextech
OKI Nextech has made innovative reforms to their manufacturing line and reduced power consumption by 74% and the amount of solder used by 70% in the process of soldering electrical components to printed circuit boards.
This production reform or "solder revolution" is led by the "point DIP" machines brought into the printed circuit board assembly line.
Until now the entire printed circuit boards had been dipped into a solder tank and the components then soldered on, requiring a large amount of power to melt the solder. The newly-introduced point DIP machines have enabled pin-point soldering at the exact locations necessary, drastically reducing the consumption of electricity and solder.
Visualization of Operational Status - 90% Energy Savings by Mode Switching

OKI Nextech, which mounts electronic components on printed circuit boards, succeeded in considerable energy savings by coupling the operation mode to the operation status of equipment.
In the process of mounting electronic components, the bond is used to temporarily fix large parts before soldering and a hardening furnace to harden the bond by heating.
As a result, the previously fixed energy consumption of the bond hardening furnace became a lean consumption that responds to fluctuations in production volume, achieving a 90% energy saving for the hardening furnace alone.
At OKI Nextech, it was impossible to lower the amount of energy used in the hardening furnace, despite a decrease in the amount of bond used due to the downsizing of parts and progression of mounting technology, which was a challenge. The reason for this was that the hardening furnace was often left in high-temperature operation mode because its operation status was not known by operators or managers.
As a countermeasure, the state of the hardening furnace was monitored by a sensor and the operator was notified by the color of a lamp on the equipment when a certain non-operation time had passed, thereby prompting the operator to switch the hibernation mode. For the case the operator does not notice the notification, we created a mechanism that allows the manager to instruct the operator in response to an automatic notification sent wirelessly to the manager’s PC.
large offices
System Development Center Receives Award for Energy-saving

The OKI System Center located in Warabi city, Saitama Prefecture, is the center of our systems development with about 2,600 workers. A large number of servers and other information communication equipment are installed here, and since it is one of the leading consumers of energy within the OKI Group, we are constantly devising ways to improve the efficiency of air conditioning and lighting here.
Specifically, we have updated the gas-fired cold/hot water generator used for air conditioning to a heat pump type, proceeded with countermeasures such as quadrupling efficiency, and realized substantial energy reductions. In 2016, we received awards from Saitama Electric Power Association and the Saitama Prefecture Governor.
Reports on misuse of public research funds and misconduct related to research
activities can also be filed from the page that opens when you click the above button.